
1 Anatomy Neupsy Key
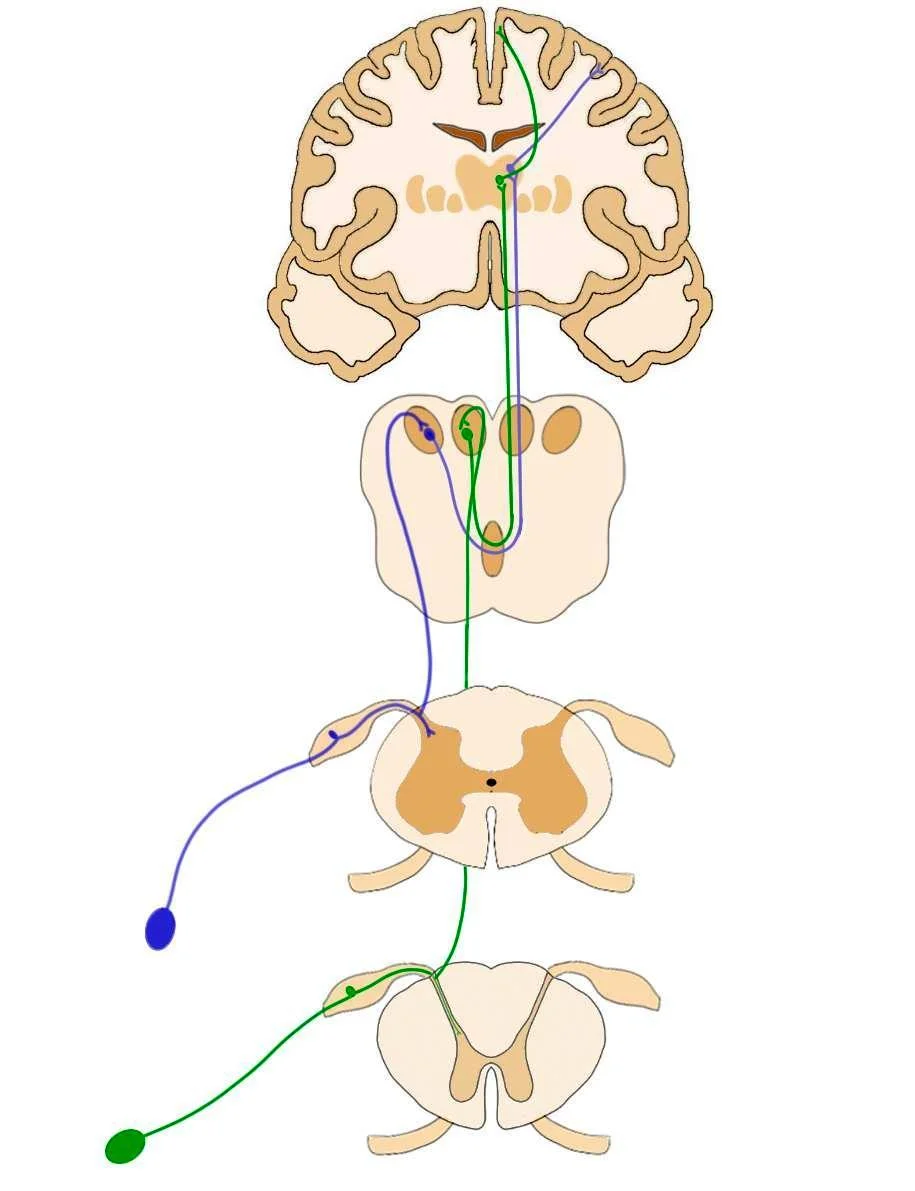
The dorsal column system (sometimes referred to as the dorsal column-medial lemniscus) and the spinothalamic tract are two major pathways that bring sensory information to the brain (Figure 14.19). The sensory pathways in each of these systems are composed of three successive neurons.. As axons of this pathway enter the dorsal column, they.
Dorsal columnsmedial lemniscus definition — Neuroscientifically Challenged
The receptive field of a dorsal column nucleus has an inhibitory surround, which is a result of the indirect connections between mechanoreceptors and the dorsal column neuron via inhibitory interneurons. A) When no stimulus is present, the dorsal column neurons fire at a baseline rate.

Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus Pathway JuanknoeCarrillo
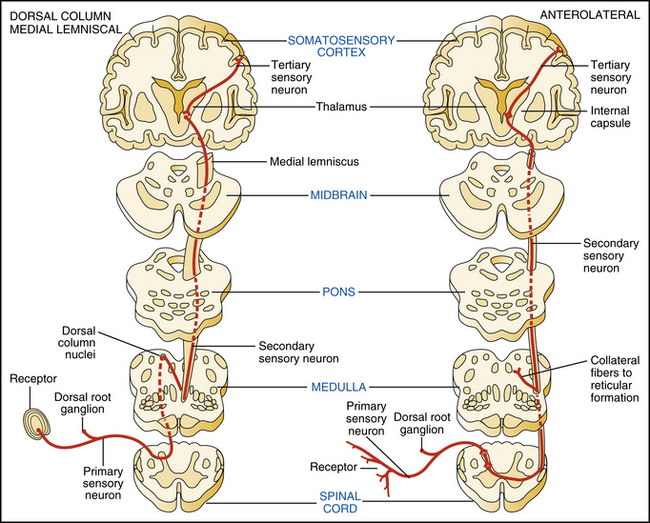
Try out our quiz to test your knowledge on posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway: Spinothalamic tracts Characteristics The spinothalamic tracts carry pain, temperature, non discriminative touch and pressure information to the thalamus. The fibers forming the spinothalamic tracts are different from the fibers of the dorsal white column in.

A) Posterior columnmedial lemniscus pathway. B) The spinothalmic pathway. Download Scientific
The Major Afferent Pathway for Mechanosensory Information: The Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscus System - Neuroscience - NCBI Bookshelf associated with each segmental spinal first-order neurons of each spinal cord and thermoceptors (see column- medial lemniscus mechanoreceptors spinothalamicanterolateral

The dorsal column medial lemniscal (DCML) pathway. Download Scientific Diagram
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway The dorsal column pathway is one of the ascending tracts i.e. the neural pathways by which sensory information from the peripheral nerves is transmitted to the cerebral cortex.
ImageQuiz Spinocerebellar & dorsal columnmedial lemniscal pathway
A neural pathway is a bundle of axons that connects two or more different neurons, facilitating communication between them. Tracts are neural pathways that are located in the brain and spinal cord (central nervous system). Each tract runs bilaterally; one on each side of the cerebral hemisphere or in a hemisection of the spinal cord.

Dorsal ColumnMedial Lemniscal and Spinothalamic Pathway Diagram Quizlet
The dorsal column, also known as the dorsal column medial lemniscus (DCML) pathway, deals with the conscious appreciation of fine touch, two-point discrimination, conscious proprioception, and vibration sensations from the entire body except for the head. In the spinal cord, this pathway travels in.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/13928/38RcTscAPai2UGazZrWBNQ_Posterior_column_medial_lemniscus_pathway.png)
Dorsal columnmedial lemniscus (DCML) pathway Anatomy Kenhub
The receptive field of a dorsal column nucleus has an inhibitory surround, which is a result of the indirect connections between mechanoreceptors and the dorsal column neuron via inhibitory interneurons. A) When no stimulus is present, the dorsal column neurons fire at a baseline rate.
The Ascending Tracts DCML Anterolateral TeachMeAnatomy
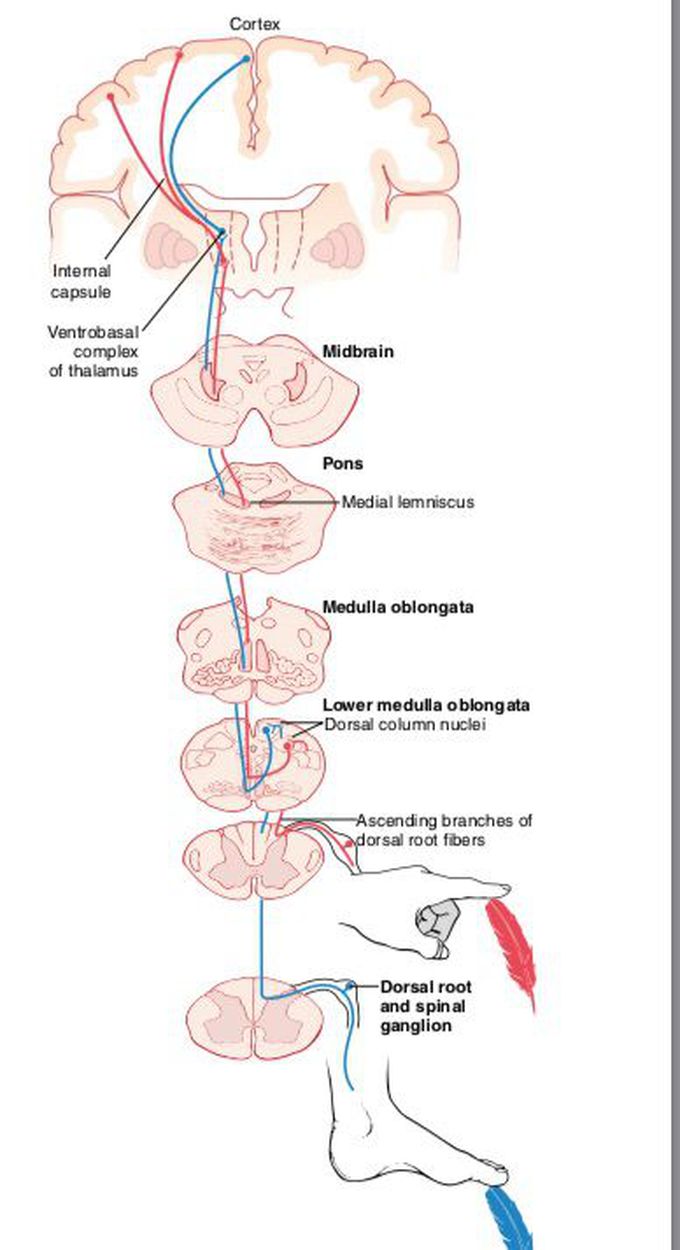
This diagram illustrates the pathway of the dorsal column medial lemniscus (posterior column pathway) in a schematic fashion. Contributed and Used with Permission from Campbell University School Of Osteopathic Medicine From: Neuroanatomy, Posterior Column (Dorsal Column) Copyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.

PPT Chapter 16 Sensory, Motor & Integrative Systems PowerPoint Presentation ID405314
The dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (DCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system. It conveys sensation of fine touch, vibration, pressure, two-point discrimination and proprioception (position) from the skin and joints. Also known as the posterior column - medial lemniscus pathway, it consists of two parts.
49 Basicmedical Key
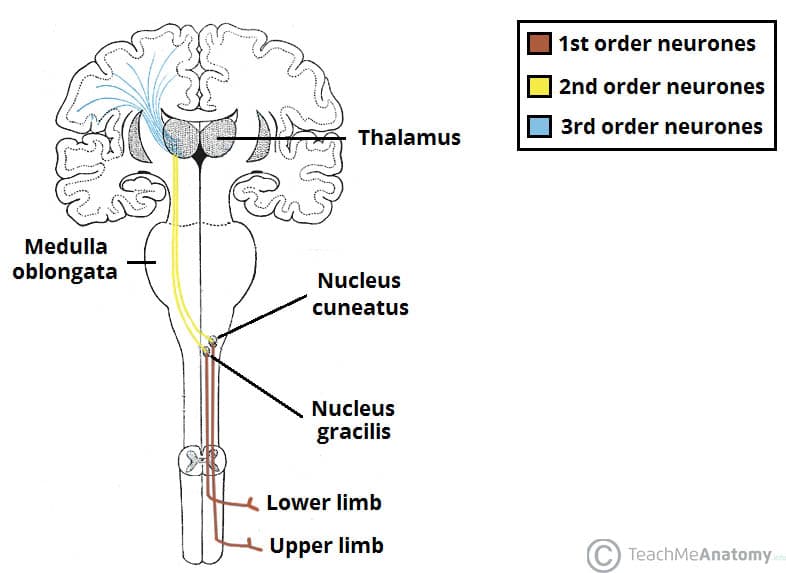
The medial lemniscus is a second-order neuron of the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway (DCML), which, with the somatotopic arrangement, transports the sensory spinothalamic information of conscious proprioception, vibration, fine touch, and 2-point discrimination of skin and joints of the body and head; from the caudal medulla to the ventra.
The dorsal columnmedial lemniscal pathway for transmitting MEDizzy
The dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway ( DCML) (also known as the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway, PCML) is a sensory pathway of the central nervous system that conveys sensations of fine touch, vibration, two-point discrimination, and proprioception (body position) from the skin and joints.

Dorsal ColumnMedial Lemnisclal Pathway and Spinothalamic Spinothalamic tract, Sensory
The primary function of the dorsal column medial lemniscus (DCML) pathway is to convey sensory information regarding fine touch, two-point discrimination, conscious proprioception, and vibration sensations to the postcentral gyrus in the cerebral cortex from our skin and joints, excluding the head. [1] [2] [3] [4] [5]

dorsal column medial lemniscus pathway animation Google Search Occupational Therapy, Physical
http://www.handwrittentutorials.com - This is the second video in a series on the major pathways in the spinal cord. This video looks at the dorsal column -.

Neural Pathways What Are They?, How, Types, Dysfunction
Dorsal column-medial lemniscus (DCML) The DCML pathway transports information about vibration, proprioception and fine touch. Information from these modalities is transported in the dorsal column, two large white matter tracts located between the dorsal grey horns of the spinal cord. These dorsal columns are divided into two regions:

Medical Education for Students Dorsal ColumnMedial Lemniscal System
This video talks about the dorsal column-medial lemniscus (DCML) sensory pathway. In this video you will learn the neuroanatomy of the DCML pathway, as well.